So, maybe you’re a budding entrepreneur, looking to create a product for the first time. Or perhaps your business struggles with launching new products because of disorganization. Whatever your situation is, everyone can benefit from using the new product development process.
What is the new product development process?
The new product development (NPD) process is a 7 stage practice to help you create a product, from idea into reality. In the software world, one can turn an idea into workable software, as either a stand-alone product, or an addition to already existing software. For each step there are certain methods or practices that will help you get the results you want.
Make your own flowchart with Gleek.
The 7 stages of new product development
Stage 1 – Idea generation
During this brainstorming stage, the goal is to get as many viable ideas as possible. How do you make the most out of your idea generation sessions? Consider these two sources for potential ideas.
Internal sources – These ideas come from within the company, through employees and their ideas or feedback.
External sources – The other place to look for new ideas is outside the company, in the form of competitors, or other entities associated with the business, such as suppliers or distributors. By far, the most valuable source of ideas is from the customers themselves.
Stage 2 – Idea screening
After you’ve come up with dozens of ideas and thrown out the ones that don’t fit, it’s time to screen the ideas, to further eliminate concepts that won’t work. Here are some common ways to know whether an idea can become a viable product.
Customer interviews – By asking the customer what problems they have with an existing product, or what they need, you gain valuable insight into the market.
Product analysis – What’s missing from the current product or software?
Competitor analysis – Is this concept already on the market? If so, how can you make it different or better?
Prioritization – Some consumer needs or problems are less important than others. Does this idea solve an urgent issue, or is it something not many people are concerned with?
Stage 3 – Concept development and testing
During this stage, several different concepts for the product must be made, with the customer in mind. The point of creating multiple concepts is to present the product to the customer in a way that will make them want to use or buy it. Two types of research are needed in order to create the best possible concepts.
Market research – The state of the economy and the target audience are important when considering the launch of a new product.
Consumer research – This type of research is to gauge how the consumer will react when presented with the product. It can be in the form of a survey, focus group, or through customer feedback.
Then comes the concept testing. Here are some ways to get feedback on your new concepts.
Focus groups – a group of people, usually more than 30 but fewer than 100, are left alone to discuss the concept and provide feedback.
Monadic testing – Like a focus group, the test subjects are left to discuss things on their own. However, each focus group receives a slightly different concept to look at.
Surveys – Asking the public questions that pertain to the concept, to gauge their feelings about it.
Comparison testing – Comparing your concept to products that already exist in a ranking system with parameters your company sets.
Concept testing and development is not a one time thing. You will likely have to make changes more than once before you get a concept that is compatible for production.
Stage 4 – Market strategy development
When information about concept testing is gathered and analyzed, the next step is to make a marketing strategy. This stage is split into three parts.
Target market, product positioning
The outcome of this part of the strategy development is to identify the target market, decide how to advertise it, and where to distribute it.
Price, budget, and distribution
The price of the product, marketing budget, and plans for distribution in the first year are set.
Long term analysis
Expectations for beyond the first year, such as profits, sales goals, and more.
Stage 5 – Product development
Finally, it’s time to create a product for demonstration purposes. This is what you will show to investors, stakeholders, and any other relevant parties. There are a few things you need to have before this stage is complete.
Minimum viable product – This is your product or software in its simplest, yet fully functioning form.
Finalize features – All of the features of the final product must be decided on.
Manufacturing cost – The cost of making or developing each unit must be calculated.
Stage 6 – Test marketing
When there is a working product that has passed all functionality tests, then it’s time to see what the customer thinks. There are a few ways to gather this information.
In house use testing – by giving people who would actually be using the product access to it, they can test it in real time and provide feedback. These potential testers can be within the company, or outside of it.
Alpha testing – Similar to in house use testing, the product is put through its paces by the development team and other employees.
Beta testing – To further work out bugs and gain feedback, testing is opened to people outside the company. Especially with games or new software, there will be plenty of volunteers willing to try out the product.
Stage 7 – Launch and commercialization
The final step is launching and commercialization. Issues such as sale price, distribution, manufacturing, and advertising are all included in the launch and commercialization. While techniques for launch vary between industries, here are some tips and techniques that can make a launch successful.
Marketing campaigns – Develop a direct marketing plan as well as an advertising strategy several weeks or months before the product launch to get the public excited and informed.
Creativity – Creativity is an important part of the launch process. The more creative your marketing and branding, the better the launch will be. Utilizing social media is a cost effective way to reach much more of your target audience.
Customer support – When a new product is available, it’s likely that there will be some issues. Having a robust customer support network helps give your company a good reputation, even if there are some bugs.
Make your own flowchart with Gleek.
We visualized 7 stages of the product development process flowchart via Gleek:
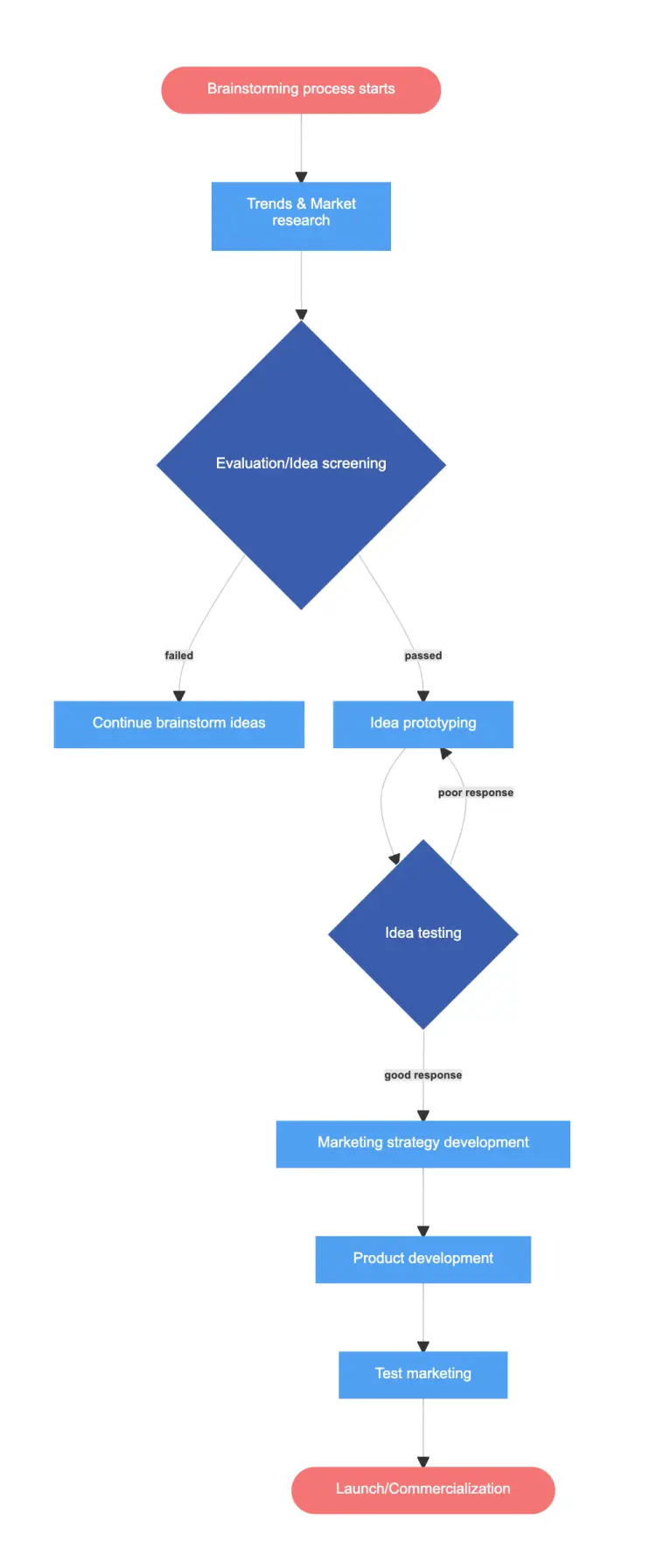
The new product development process is a tried and true method that will make innovation and creation go smoothly, and boosts your chances of success on the market. With all business comes the need for charts and diagrams. Gleek is a text-based diagramming tool used by software developers and other business professionals to quickly create easy-to-read diagrams. Get started for free here. Looking for more flowchart examples? You can find them in the 20 editable flowchart templates blog post.
Related posts
Uses for cross-functional flowcharts
How to Use Flowcharts for Problem Solving
Flowcharts for Decision-Making: Visualizing Options and Risks
What are flowchart symbols? Here’s a handy guide with examples
A step-by-step guide to creating a flowchart in Google Docs
